In Windows 10, the Windows Recovery Environment has become a very sophisticated, almost eerily intelligent fix-everything program that works very well. Except, of course, when it doesn't.
You know you're in the Windows Recovery Environment if you see a blue Choose an Option screen or a blue Troubleshoot screen like the one shown here. (If you find yourself facing a blue Choose an Option screen, choose Troubleshoot!)
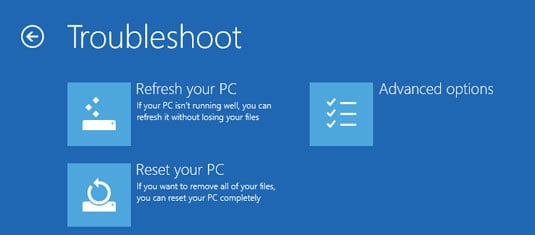
From the Troubleshoot screen, you can run Refresh or Reset directly: You can also choose Advanced Options, which brings you to several interesting — if little-used — options, as shown here.
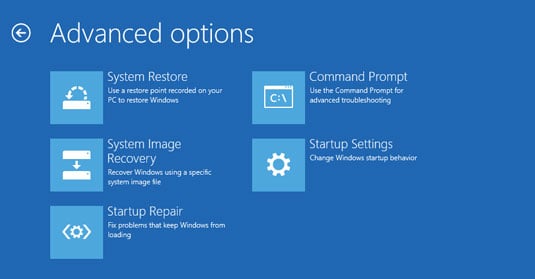
You can also get to this screen by choosing Advanced Startup from the Recovery list. After you choose Advanced Startup, choose Troubleshoot and then choose Advanced Options.
Here's what the Advanced Options can do:
System Restore puts your system back to a chosen restore point. It won't work, though, unless you've turned on System protection/restore points for one or more drives on your computer.
System Image Recovery requires a system image file that you can make only by using the DOS command line in a very geeky way. The particular command you need is recimg.exe. Details at the Windows 10 forums.
Startup Repair reboots into a specific Windows Recovery Environment program known as Start Repair and runs a diagnosis and repair routine that seeks to make your PC bootable again. A Start Repair log file is generated at WindowsSystem32LogfilesSrtSrtTrail.txt. If you find yourself running Automatic Repair, you can't do anything: Just hold on and see whether it works.
Command Prompt brings up an old-fashioned DOS command prompt, just like you get if you go into Safe Mode. Only for the geek at heart. You can hurt yourself in there.
Startup Settings reboots Windows and lets you go into Safe Mode, change video resolution, start debugging mode or boot logging, run in Safe Mode, disable driver signature checks, disable early launch anti-malware scans, and disable automatic restart on system failure. Definitely not for the faint of heart.
If you ever wondered how to do an old-fashioned "F8" boot into Safe Mode, now you know.

