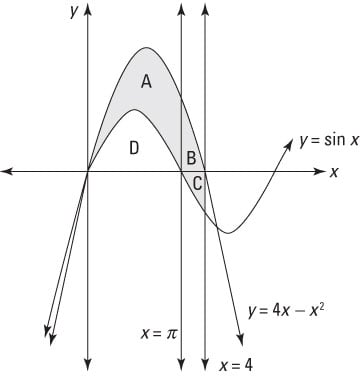
You can use the concept of unsigned area to measure the area between curves. For example, you can use this technique to find the unsigned shaded area in the following figure.
In this example, you will approximate your answer to two decimal places using
The first step is to find an equation for the solution (which will probably give you partial credit), and then worry about solving it.
First, split the shaded area into three regions labeled A, B, and C. You should also label region D, which you need to consider. Notice that x = separates regions A and B, and the x-axis separates regions B and C.
You could find three separate equations for regions A, B, and C, but there’s a better way.
To measure the unsigned area between two functions, use this quick trick:
Area = Integral of Top Function – Integral of Bottom Function
That’s it! Instead of measuring the area above and below the x-axis, just plug the two integrals into this formula. In this problem, the top function is 4x – x2 and the bottom function is sin x:
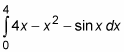
This evaluation isn’t too horrible:
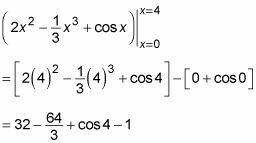
When you get to this point, you can already see that you’re on track, because the professor was nice enough to give you an approximate value for cos 4:
So the unsigned area between the two functions is approximately 9.02 units.
If the two functions change positions — that is, the top becomes the bottom and the bottom becomes the top — you may need to break the problem up into regions. But even in this case, you can still save a lot of time by using this trick.
Here’s another example: Find the area between y = x and
as shown in this figure.
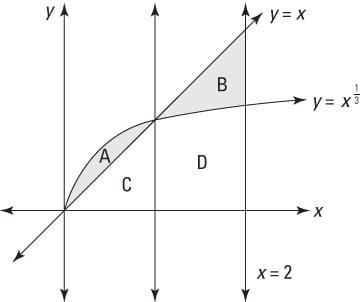
First, measure the shaded area from the figure by using four separate regions. Here’s how to do it using the top-and-bottom trick.
Notice that the two functions cross at x = 1. So from 0 to 1, the top function is
and from 1 to 2 the top function is x. So set up two separate equations, one for region A and another for the region B:
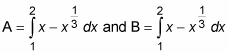
When the calculations are complete, you get the following values for A and B:
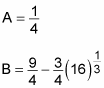
Add these two values together to get your answer:
As you can see, the top-and-bottom trick gets you the same answer much more simply than measuring regions.

