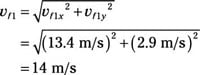Collisions can take place in two dimensions. For example, soccer balls can move any which way on a soccer field, not just along a single line. Soccer balls can end up going north or south, east or west, or a combination of those. So you have to be prepared to handle collisions in two dimensions.
Sample question
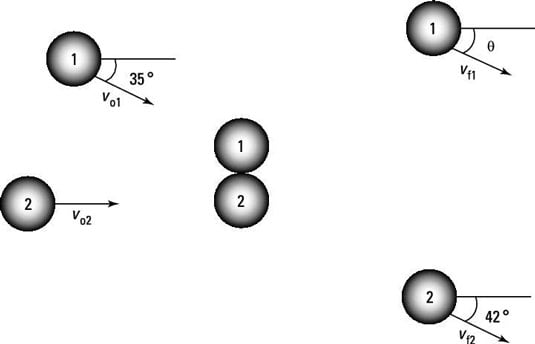
In the figure, there’s been an accident at an Italian restaurant, and two meatballs are colliding. Assuming that vo1 = 10.0 m/s, vo2 = 5.0 m/s, vf2 = 6.0 m/s, and the masses of the meatballs are equal, what are theta and vf1?
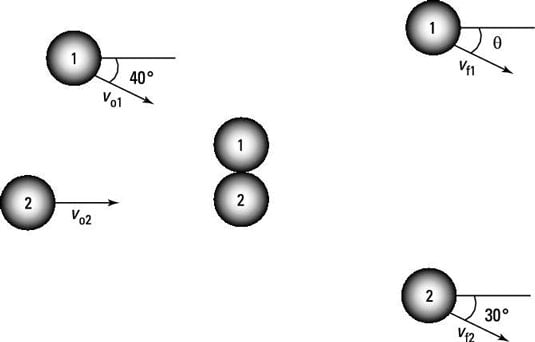
The correct answer is theta = 24 degrees and vf1 = 8.2 m/s.
You can’t assume that these meatballs conserve kinetic energy when they collide because the meatballs probably deform from the collision. However, momentum is conserved. In fact, momentum is conserved in both the x and y directions, which means
pfx = pox
and
pfy = poy
Here’s what the original momentum in the x direction was:
pfx = pox = m1vo1 cos 40 degrees + m2vo2
Momentum is conserved in the x direction, so you get
pfx = pox = m1vo1 cos 40 degrees + m2vo2 = m1vf1x + m2vf2 cos 30 degrees
Which means that
m1vf1x = m1vo1 cos 40 degrees + m2vo2 – m2vf2 cos 30 degrees
Divide by m1:
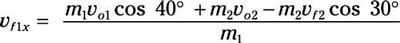
And because m1 = m2, this becomes
vf1x = vo1 cos 40 degrees + vo2 – vf2 cos 30 degrees
Plug in the numbers:
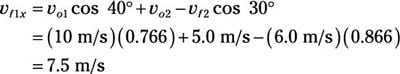
Now for the y direction. Here’s what the original momentum in the y direction looks like (in the downward direction):
pfy = poy = m1vo1 sin 40 degrees
Set that equal to the final momentum in the y direction:
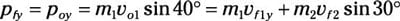
That equation turns into:
m1vf1y = m1vo1 sin 40 degrees – m2vf2 sin 30 degrees
Solve for the final velocity component of meatball 1’s y velocity:
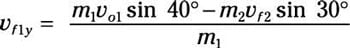
Because the two masses are equal, this becomes
vf1y = vo1 sin 40 degrees – vf2 sin 30 degrees
Plug in the numbers:
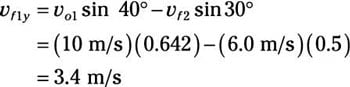
So:
vf1x = 7.5 m/s (to the right)
vf1y = 3.4 m/s (downward)
That means that the angle theta is

And the magnitude of vf1 is

Practice questions
Assume that the two objects in the preceding figure are hockey pucks of equal mass. Assuming that vo1 = 15 m/s, vo2 = 7.0 m/s, and vf2 = 7.0 m/s, what are theta and vf1, assuming that momentum is conserved but kinetic energy is not?
Assume that the two objects in the following figure are tennis balls of equal mass. Assuming that vo1 = 12 m/s, vo2 = 8.0 m/s, and vf2 = 6.0 m/s, what are theta and vf1, assuming that momentum is conserved but kinetic energy is not?
Following are answers to the practice questions:
14 m/s, 26 degrees
Momentum is conserved in this collision. In fact, momentum is conserved in both the x and y directions, which means the following are true:
pfx = pox
pfy = poy
The original momentum in the x direction was
pfx = pox = m1vo1 cos 40 degrees + m2vo2
Momentum is conserved in the x direction, so
pfx = pox = m1vo1 cos 40 degrees + m2vo2 = m1vf1x + m2vf2 cos 30 degrees
Solving for m1vf1x gives you:
m1vf1x = m1vo1 cos 40 degrees + m2vo2 – m2vf2 cos 30 degrees
Divide by m1:
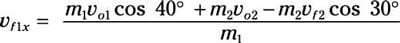
Because m1 = m2, that equation becomes
vf1x = vo1 cos 40 degrees + vo2 – vf2 cos 30 degrees
Plug in the numbers:
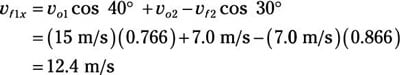
Now for the y direction. The original momentum in the y direction was
pfy = poy = m1vo1 sin 40 degrees
Set that equal to the final momentum in the y direction:
pfy = poy = m1vo1 sin 40 degrees = m1vf1y + m2vf2 sin 30 degrees
Which turns into
m1vf1y = m1vo1 sin 40 degrees – m2vf2 sin 30 degrees
Solve for the final velocity component of puck 1’s y velocity:
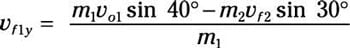
Because the two masses are equal, the equation becomes
vf1y = vo1 sin 40 degrees – vf2 sin 30 degrees
Plug in the numbers:
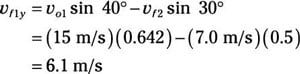
So
vf1x = 12.4 m/s
vf1y = 6.1 m/s
That means the angle theta is
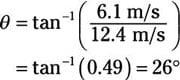
And the magnitude of vf1 is
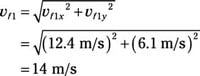
14 m/s, 12 degrees
In this situation, momentum is conserved in both the x and y directions, so the following are true:
pfx = pox
pfy = poy
The original momentum in the x direction was
pfx = pox = m1vo1 cos 35 degrees + m2vo2
Momentum is conserved in the x direction, so:
pfx = pox = m1vo1 cos 35 degrees + m2vo2 = m1vf1x + m2vf2 cos 42 degrees
Which means:
m1vf1x = m1vo1 cos 35 degrees + m2vo2 – m2vf2 cos 42 degrees
Divide by m1:
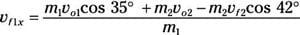
Because m1 = m2, this becomes
vf1x = vo1 cos 35 degrees + vo2 – vf2 cos 42 degrees
Plug in the numbers:
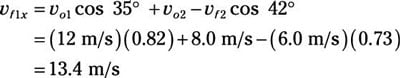
Now for the y direction. The original momentum in the y direction was
pfy = poy = m1vo1 sin 35 degrees
Set that equal to the final momentum in the y direction:
pfy = poy = m1vo1 sin 35 degrees = m1vf1y + m2vf2 sin 42 degrees
Solving for m1vf1y gives you:
m1vf1y = m1vo1 sin 35 degrees – m2vf2 sin 42 degrees
Solve for the final velocity component of puck 1’s y velocity:
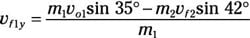
Because the two masses are equal, the equation becomes
vf1y = vo1 sin 35 degrees – vf2 sin 42 degrees
Plug in the numbers:
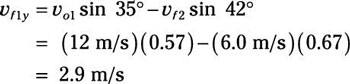
So:
vf1x = 13.4 m/s
vf1y = 2.9 m/s
Which means the angle theta is
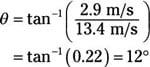
And the magnitude of vf1 is