Targeted therapy causes less harsh or toxic side effects because it does not affect healthy rapidly dividing cells.
The most well-known targeted therapy is trastuzumab (marketed as Herceptin), a medicine that kills specific cancer cells that are HER2+ (HER2-positive). A protein called human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), which is found on the surface of the cancer cell, in large quantities can promote the rapid growth of cancer cells. Approximately 20–25 out of every 100 patients with breast cancer are HER2+ and are most likely to respond well to Herceptin treatment.This figure illustrates HER2 receptors.
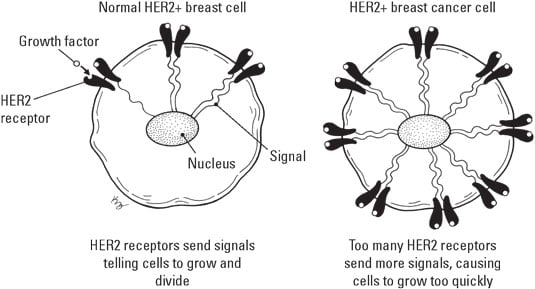 Illustration by Kathryn Born
Illustration by Kathryn BornHow cancer disrupts HER2+ breast cells.
It's difficult to predict how any one person will respond to a treatment. Therefore, targeted therapies were developed based on a particular group of factors that may be found on a tumor. Herceptin treatment was made possible through the results from clinical trials that show specific therapies to be more effective on certain types of breast cancer cells. Clinical trials have shown that Herceptin reduces the risk of HER2-positive breast cancers from coming back. In other words, individuals with HER2+ breast cancer get personalized treatment, which is as a result of precision medicine.
This figure illustrates how Herceptin works on HER2+ breast cancer cells.
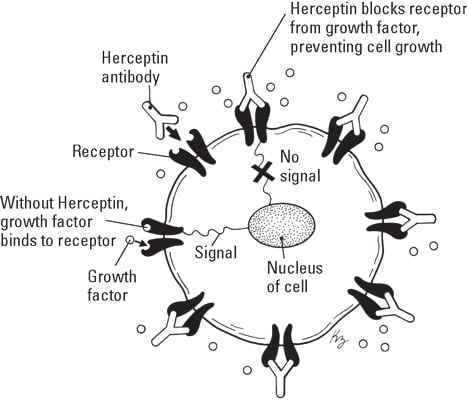 Illustration by Kathryn Born
Illustration by Kathryn BornHerceptin (antibody) action on HER2+ breast cancer.
Other targeted therapies besides Herceptin include the following:
- Bevacizumab (marketed as Avastin): Used to treat colon cancer and ovarian cancer.
- Lapatinib: Used to treat HER2+ metastatic breast cancer.
- Everolimus (marketed as Afinitor): Used to treat kidney cancer, breast cancer, and brain cancer.
- Pertuzumab (marketed as Perjeta): Used in combination with Herceptin and/or Taxotere to treat metastatic breast cancer.
- T-DM1 (marketed as Kadcyla): Used to treat HER2+ metastatic breast cancer.
- Denosumab (marketed as Xgeva): Used for treatment of secondary breast cancer in the bone.

